Gaurav Jha
Allen High School
Advanced Computer Science III
Mr.Ben-Yaakov
September 2, 2022
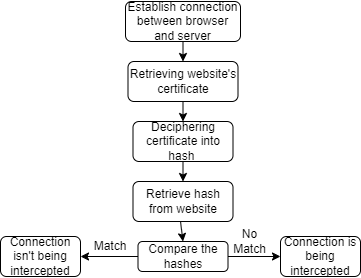
During the early years of the internet the standard application protocol , how clients and servers interact, used was HTTP. However, due to the overly curious nature of individuals with malicious intent, security became a major concern. The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) was quickly unveiled as unreliable due to the lack of safety and authentication. This led to the birth of Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS). The two primary purposes of the new application protocol was the need for security and privacy. (GRC 2020) Unlike the original, HTTPS inscribed the web connections and verify the legitimacy of the website. One way that this authenticity is recognized, is through certificate authorities. CAs allows for orginizations to verify the validity of a webpage by seeing the legal papers from the owners face-to-face. This was essential to develop because the HTTP was susceptible to MITM attacks and redirection of information. Man In The Middle (MITM) is when the connection between the user and the web application is broken by literally a “middle man”, in which a new connection is established through the attacker. MITM attack are detrimental and pose countless risks. For example when banking and giving account details to a bank employee, the attack can eavesdrop with the help of the new connection and retrieved information they shouldn’t know. In addition to this, MITM can lead to identity theft as well as introduce malware to computers. CAs overcome this problem as they allow the user to safely interact with the webpage if given the correct certification. However, HTTPS Proxy Applications resurface this problem as they redirect the user and they allow or block the user from traversing the site. A real life example as a high school student is GoGuardian. GoGuardian is used by schools to monitor students activity and filter content they access. While some may question the morality, schools and governments have the right to spy on you. SSL interceptions can be reliably recognized and addressed even though they cannot be prevented by conventional means. An SSL interception can be identified by looking at the certificate's fingerprint. If the certificate is altered in any way, a new fingerprint/hash , appears, indicating that the communication is being intercepted. Fundamentally, these fingerprints are programs that examine the SSL Certificate's data. In order to demonstrate that the fingerprint has changed, a strong hash will change almost entirely even when the SSL certificate information is slightly altered. Huge websites that have several certificates for a multitude of pages may experience False-Positive. As a result, when individuals accessing such sites notice that they are receiving the incorrect SSL hash, they will assume that their connection is being monitored even though the website was actually using numerous certificates. (GRC 2020) In conclusion, society needs to become more aware of their connection and privacy when using the internet.
References
Steve, S., & Gibson, G. R. (n.d.). Grc | SSL tls HTTPS web server certificate fingerprints. Gibson Research Corporation. https://www.grc.com/fingerprints.htm#top